S Wave Velocity Equation Determining Earthquake Distance
The restoring forces on a vibrating string proportional to curvature.
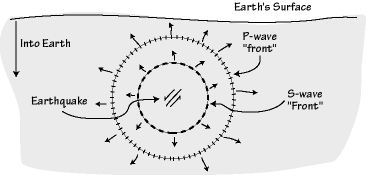
S wave velocity equation. In seismology s waves secondary waves or shear waves sometimes called elastic s waves are a type of elastic wave and are one of the two main types of elastic body waves so named because they move through the body of an object unlike surface waves. The wave moves through elastic media and the main restoring force comes from shear effects. Kr turns out to be the velocity of propagation. This equation determines the properties of most wave phenomena not only light waves.
Seismology and the earths deep interior the elastic wave equation equations of motion equations of motion pp waves waves r2ul2uu uu t let us apply the divoperator to this equation we obtain r2ol2uo t where ouiui or o a o 2 2 1 t r l u a 2 p wave velocity acoustic. The wave equa tion is a second order linear hyperbolic pde that describesthe propagation of a variety of waves such as sound or water waves. A simple method of predicting s wave velocity. Chapter 4 the wave equation another classical example of a hyperbolic pde is a wave equation.
The mathematics of pdes and the wave equation. In many real world situations the velocity of a wave. . A reflected p wave a refracted p wave a reflected converted s wave and a refracted converted s wave.
Article pdf available in geophysics 716 november 2006 with 1785 reads how we measure reads a read is counted each time someone views a. The wave equation in one dimension later we will derive the wave equation from maxwells equations. The angles of reflection and refraction for the converted ray paths can also be calculated using snells law. For the general case each layer should have a p wave velocity and an s wave velocity.
Here it is in its one dimensional form for scalar ie non vector functions f. The electromagnetic wave equation is a second order partial differential equation that describes the propagation of electromagnetic waves through a medium or in a vacuumit is a three dimensional form of the wave equationthe homogeneous form of the equation written in terms of either the electric field e or the magnetic field b takes the form. The seismic wave equation using the stress and strain theory developed in the previous chapter we now con struct and solve the seismic wave equation for elastic wave propagation in a uniform whole space. S waves are transverse waves meaning that the oscillations of an s waves particles are perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation.
The s wave moves as a shear or transverse wave so motion is perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation. Lets do it again from an action integral. We will show that two types of solutions are possible corresponding to compressional p and shear s waves and we will derive the equations for their velocities that we presented in the.